ICP-OES
Optical emission spectroscopy with inductively coupled plasma (ICP-OES) is used for the routine analysis of elements in aqueous solutions in the concentration range mg/L to µg/L. The method allows the simultaneous determination of all metals and some non-metals (up to 70 elements) from acidified, aqueous solutions up to a total dissolved substance content of approx. 1 g/L.

ICP-MS
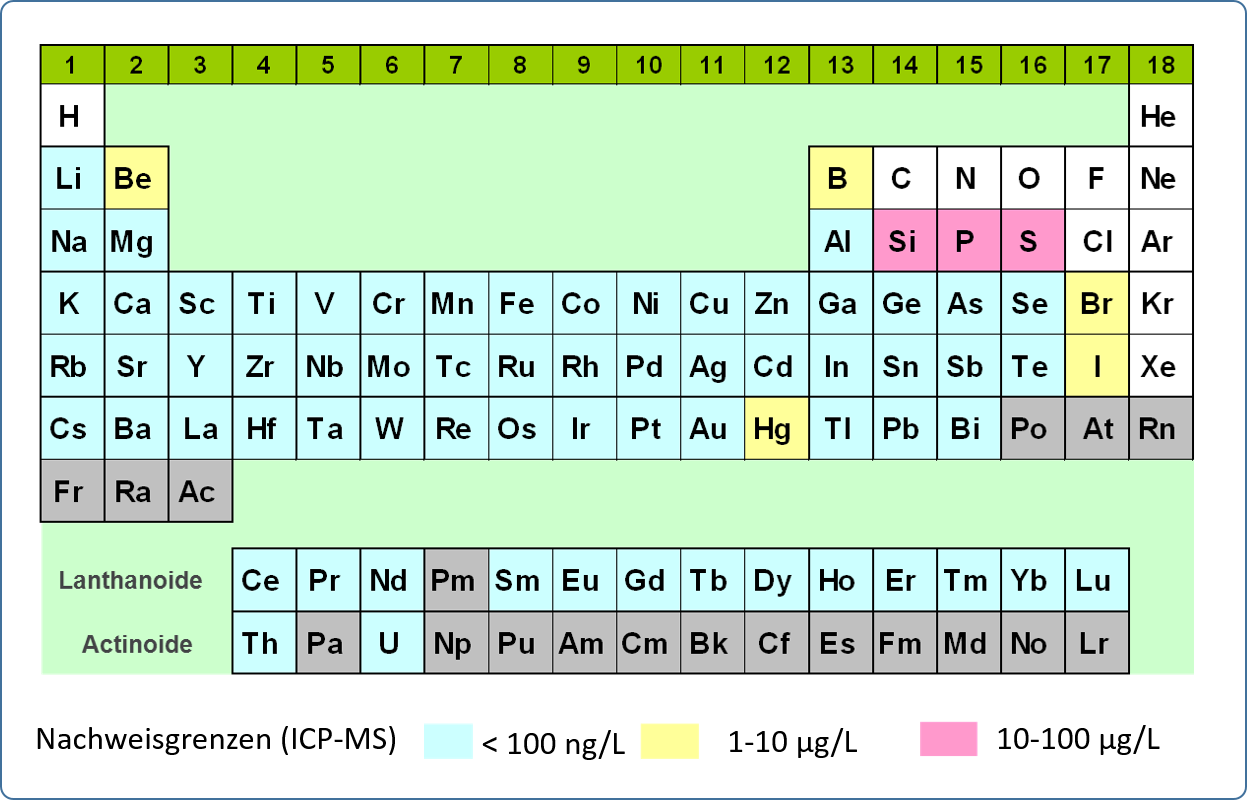
Mass spectrometry with inductively coupled plasma (ICP-MS) is used for the analysis of trace elements and the isotopic composition of elements in aqueous solutions in the concentration range µg/L to ng/L. The method allows the simultaneous determination of nearly all metals and some non-metals (up to 70 elements) from acidified aqueous solutions up to a total dissolved substance content of approx. 1 g/L.

Sample collection and sample preparation
Aqueous samples are filtered with a 0.45 µm filter and immediately after sampling acidified to 1-5 vol.% with highly pure, concentrated nitric acid and stored in sample bottles made of inert plastic (PE, FEP or PFA) to exclude element losses due to precipitation or adsorption on the vessel material. The samples can then be analysed directly in the laboratory without further preparation.
Measuring principle for ICP-OES
In ICP-OES analysis, the sample solution is introduced into an inductively coupled argon plasma via a pneumatic atomisation system. At a temperature of 6000-8000 K in the plasma the elements are excited and ionised. By emitting an element-specific radiation (wavelength), they then return to their ground state, whereby the wavelength (resolution in the range of 0.005 nm) of the emitted radiation is element-specific. The quantitative determination is based on the proportionality of radiation intensity and element concentration in calibration and analyte solutions. Thus, analytes in the medium concentration and trace range can be determined in aqueous or digestion solutions.
ICP-MS Measuring principle
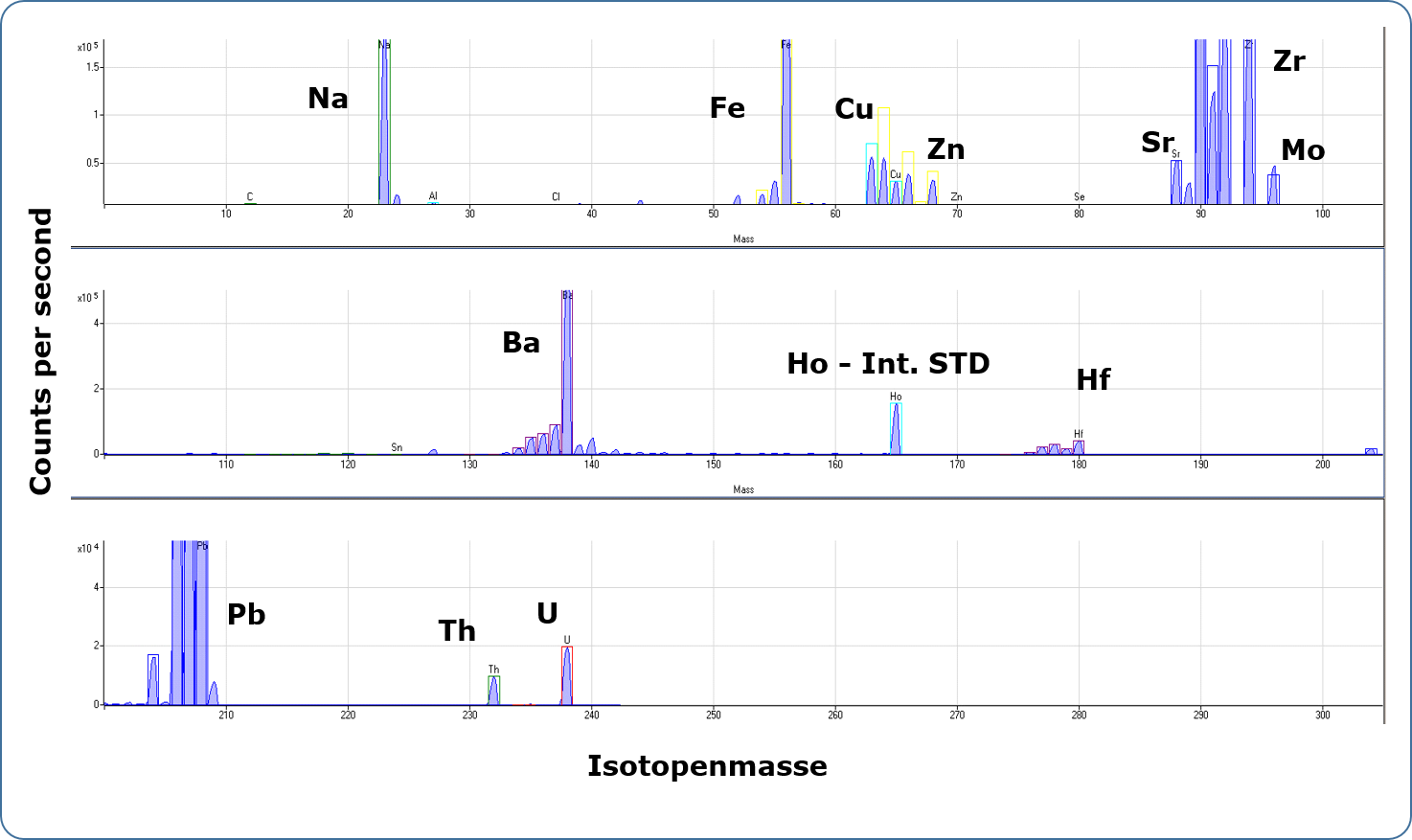
In ICP-MS analysis, the sample solution is also introduced into an inductively coupled argon plasma via a pneumatic atomisation system. At a temperature of 6000-8000 K in the plasma, the elements are excited and ionised. The degree of ionisation of many elements is more than 50% at these temperatures. The present single positively charged ions pass through two pinholes (sampler and skimmer cone) via an electrostatic lens system into the high vacuum of the quadrupole mass spectrometer. If necessary, interfering molecular ions can be separated by a collision cell connected upstream. In the quadrupole, the ions or isotopes are separated according to their mass-to-charge ratio and detected by a sensitive charge-sensitive detector (dual mode SEV). The measurement signals on the individual isotope masses (element lithium-6 to uranium-238, resolution approx. 0.3 amu) are recorded sequentially and evaluated by a computer. For quantitative determination of the element content of a solution, the device is calibrated with standard solutions of known content.
Information on the analysis of metals in auqeous solutions via ICP-MS
The following things should be considered when giving samples:
- The filtered samples should be in an aqueous, clear solution
- The carbon content (organic as well as inorganic) should be < 1%
- The samples should be acidified, please use concentrated nitric acid (65% HNO3; suprapure purity or comparable) (can be provided)
- As sample vessels please use clean and dry plastic vessels (see Glass vessels can lead to falsified results due to bleeding of various cations from the glass
- Please add a blank (contains everything in exactly the same ratio as the sample, except for the analytes to be analysed)
Example Blank: An aqueous washing solution of a brass bath (CuZn alloy) is to be tested for copper and zinc.
- The sample contains the solution after the washing step including the added nitric acid.
- The blank contains the washing solution before the washing step including the added nitric acid.
Only if both samples are present, the difference can be used to determine the exact amount of zinc and copper dissolved by the rinsing step.

Requests and contact
Prof. Dr. Ralf Kautenburger
Universität des Saarlandes
Anorganische Chemie
Elementanalytik - WASTe
Campus C4 1, Room -1.06
66123 Saarbrücken
Phone: +49 681 302-2171
Fax: +49 681 302-70655
r.kautenburger(at)mx.uni-saarland.de