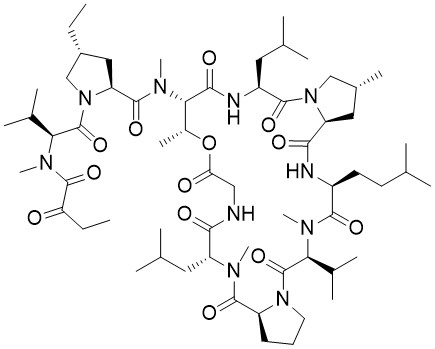
Mycoplanecin A
Mycoplanecin A, first isolated in 1983 from the fermentation broth of Actinoplanes awajinensis subsp. mycoplanecinus. Despite its early discovery, significant renewed interest in mycoplanecin A has emerged by recent investigations. These studies confirmed its remarkable potency against Mtb with a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) significantly lower than that of the related griselimycins.
A. Torikata, R. Enokita, T. Okazaki, M. Nakajima, S. Iwado, T. Haneishi, M. Arai, J. Antibiot. 1983, 36, 957–960.
M. Nakajima, A. Torikata, Y. Ichikawa, T. Katayama, A. Shiraishi, T. Haneishi, A. Mamoru, J. Antibiot. 1983, 36, 961–966.
C. Fu, Y. Liu, C. Walt, S. Rasheed, C. D. Bader, P. Lukat, M. Neuber, F. P. J. Haeckl, W. Blankenfeldt, O. V. Kalinina, R. Müller, Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 791.
The first total synthesis of mycoplanecin A, a potent antitubercular macrocyclic depsipeptide natural product targeting the DnaN sliding clamp, is described. Interesting key steps are the synthesis of the two trans-4-alkylated-L-prolines via an iterative Matteson homologation and an O→N acyl shift observed during the fragment coupling of the building blocks. The challenging macrocyclization of the globally deprotected linear precursor was accomplished under optimized high-temperature, high-dilution conditions. This work provides chemical access to mycoplanecin A, enabling further biological investigation and analogue development against the important pathogen Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- E. Papadopoulos, U. Kazmaier, "Total Synthesis of Mycoplanecin A", Org. Lett. 2025, 27, 9061–9065. DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.5c02803